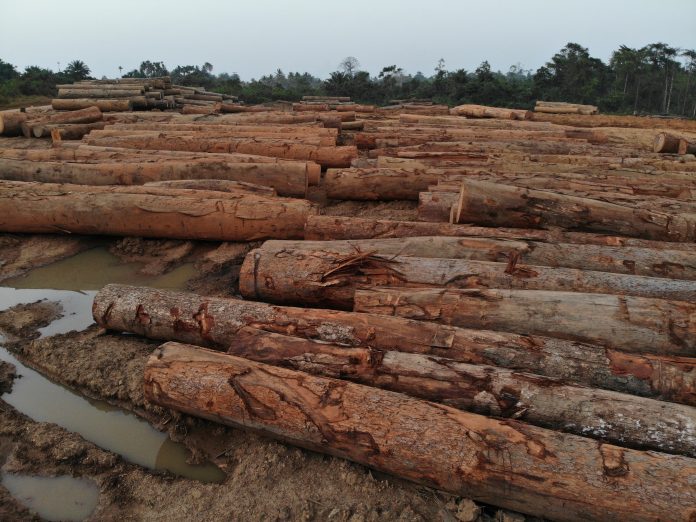
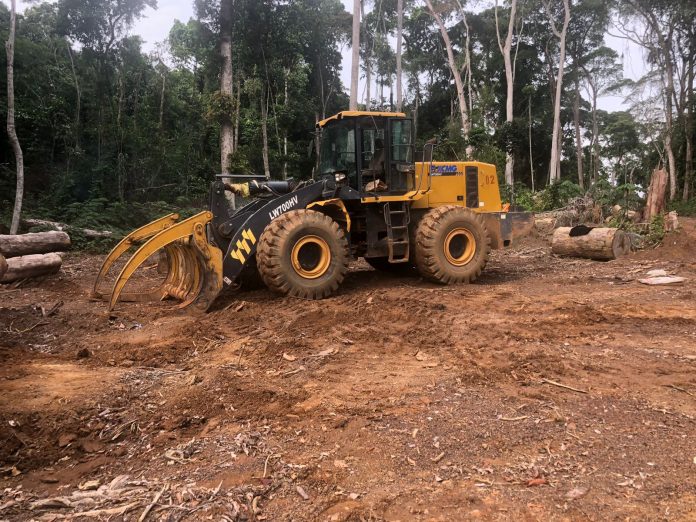
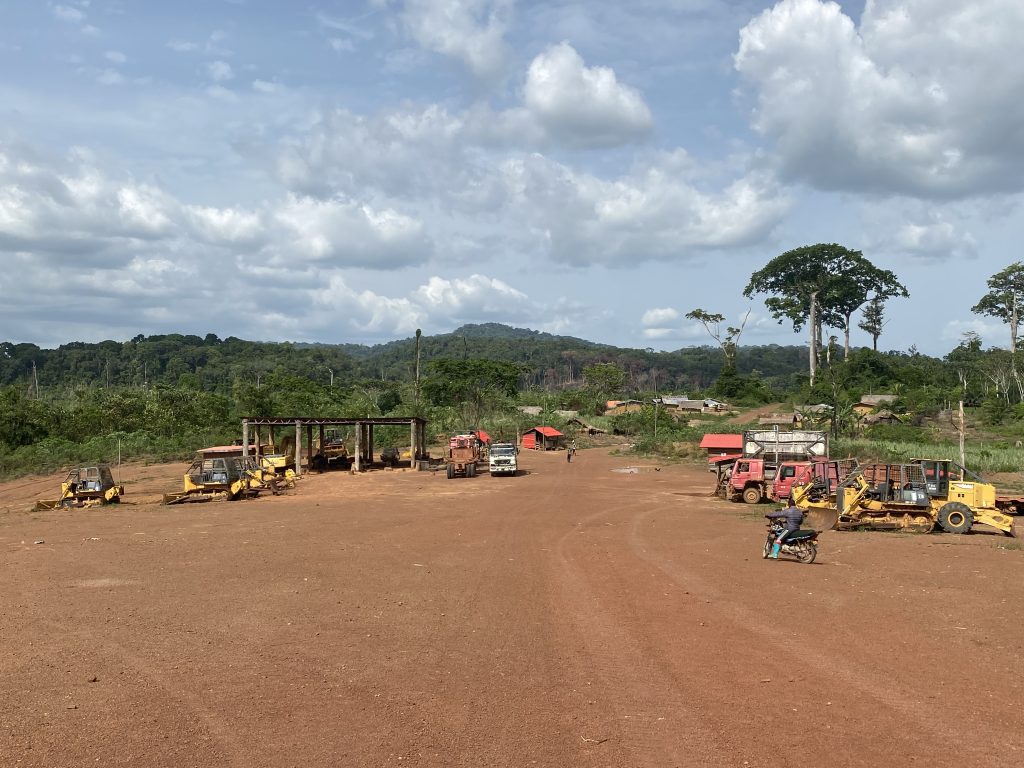
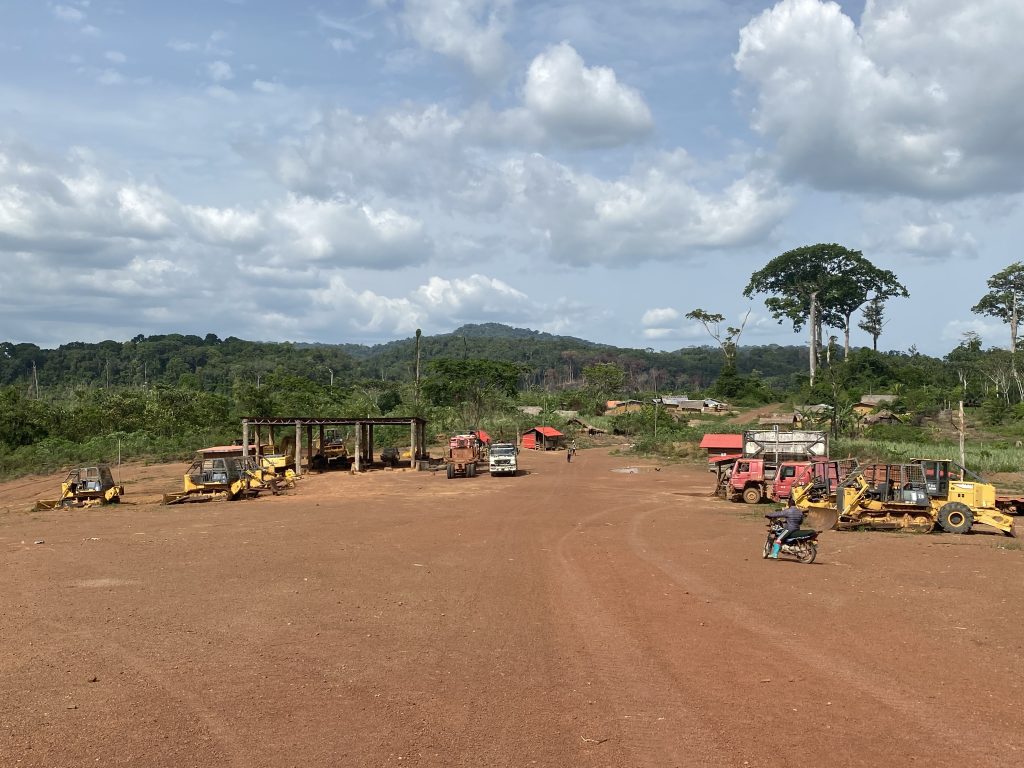
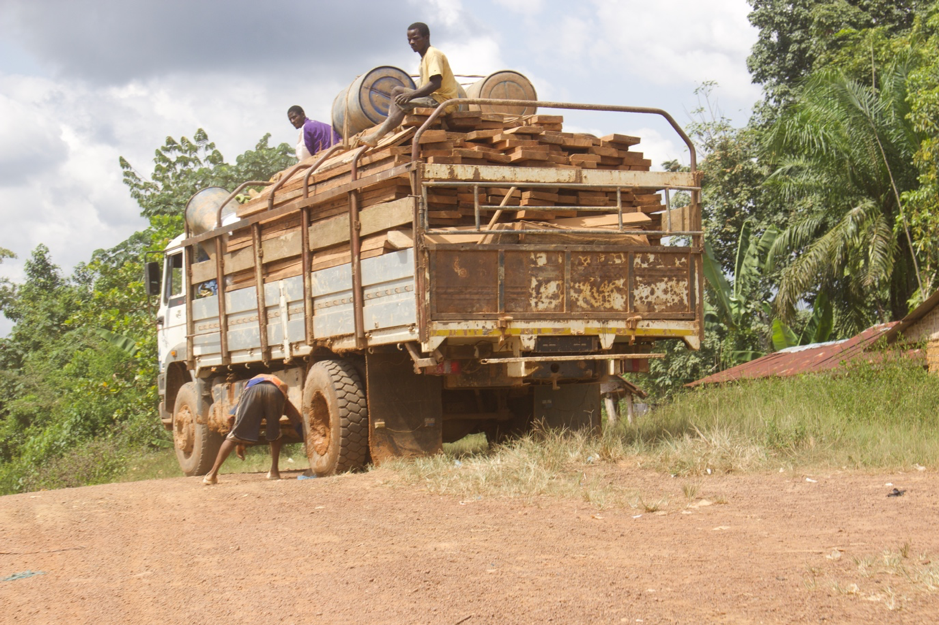
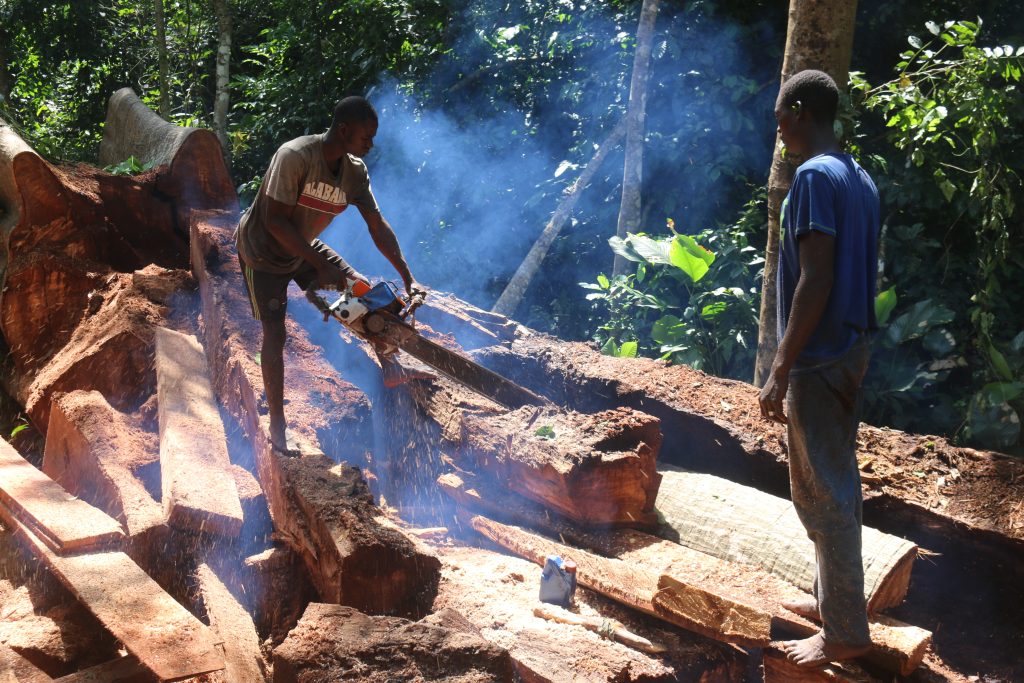
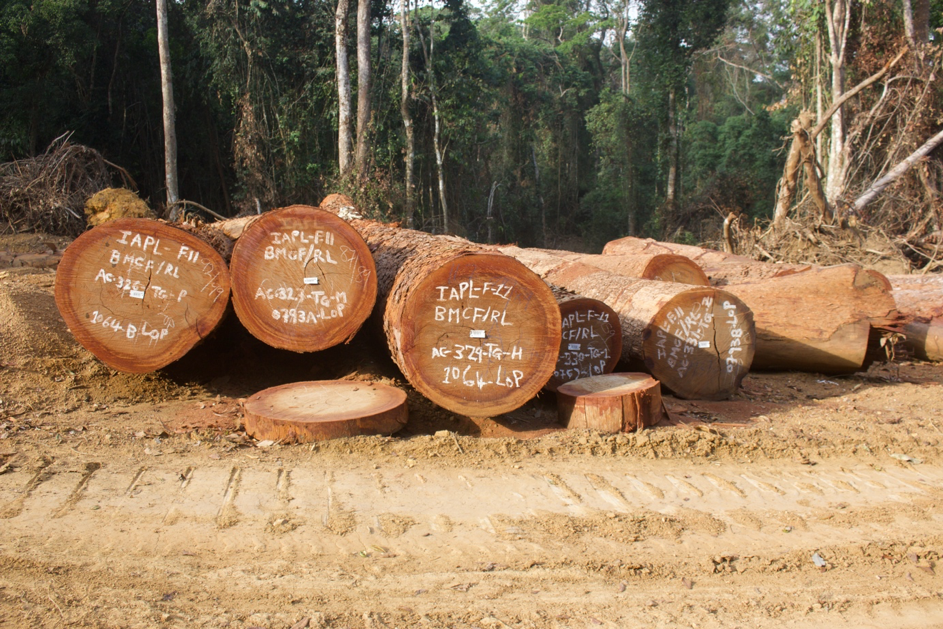
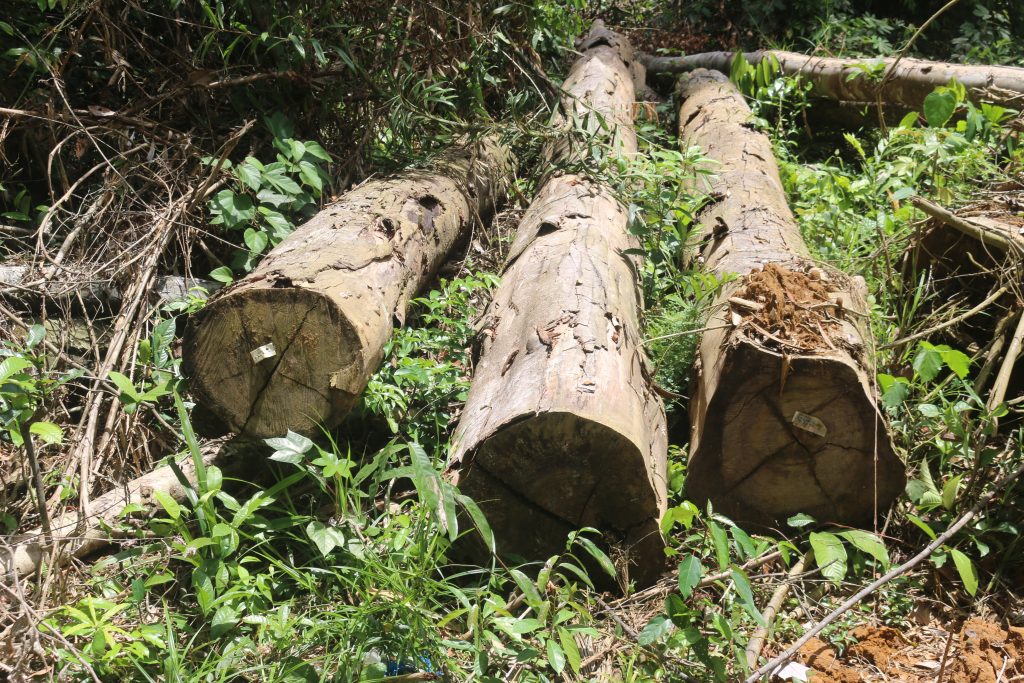
Top: The Forestry Development Authority (FDA) permitted West Water Group (Liberia) to export 797 logs in March. However, over half of the consignment was illegally harvested. The DayLight/Derick Snyder
By James Harding Giahyue and Derick Snyder
Editor’s Note: This is the fourth part of a series on the Forestry Development Authority’s approval of illegal timber exports.
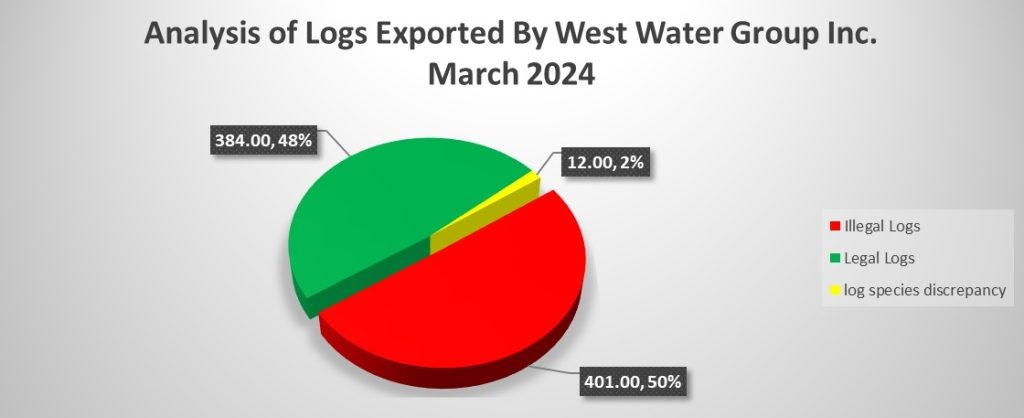
- In February, the FDA’s log-tracking computer LiberTrace red-flagged 413 logs in West Water’s consignment with multiple problems. Yet the Forestry Development Authority ignored the warnings and approved the shipment.
- The FDA dismisses DayLight’s initial investigation of the illegal export as an “intentional misinterpretation” of the facts
- But DayLight traced some of the illegal logs back to the stumps of the trees from which they were harvested, supporting LiberTrace’s findings
- A relook at the LiberTrace analysis found several discrepancies, indicating a cover-up
- Last year, West Water did not have a valid harvesting certificate, FDA’s records reveal
- The illegal approval reduced government taxes on the logs and encouraged unsustainable logging and impunity
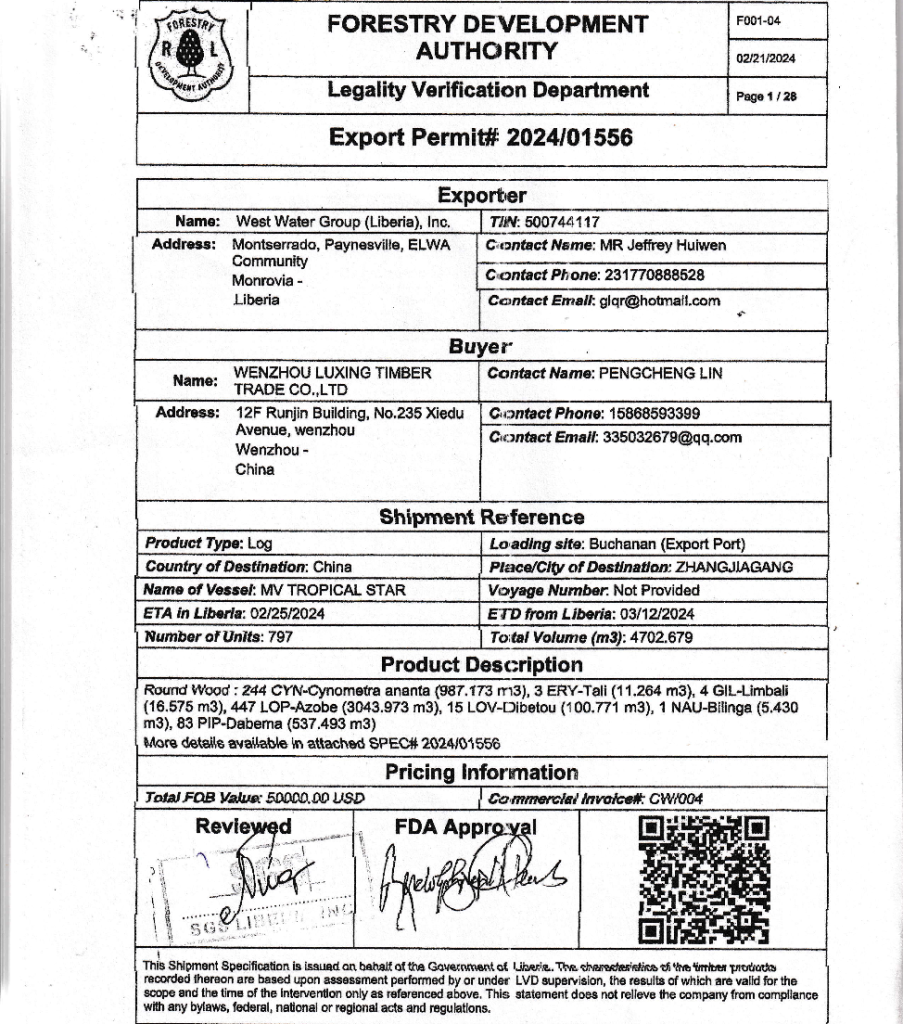
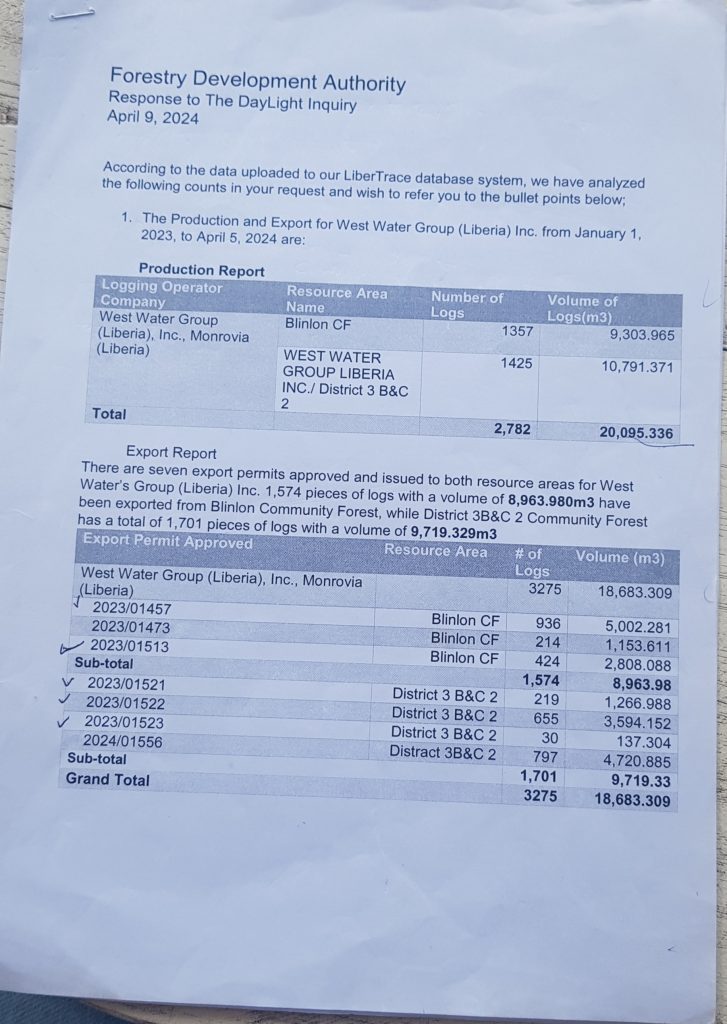
GAYEPUEWHOE TOWN, Grand Bassa County – Last month, a DayLight investigation uncovered the Forestry Development Authority (FDA) approved the export of 797 logs (4,702.679 cubic meters) valued at an estimated US$1 million for a company.
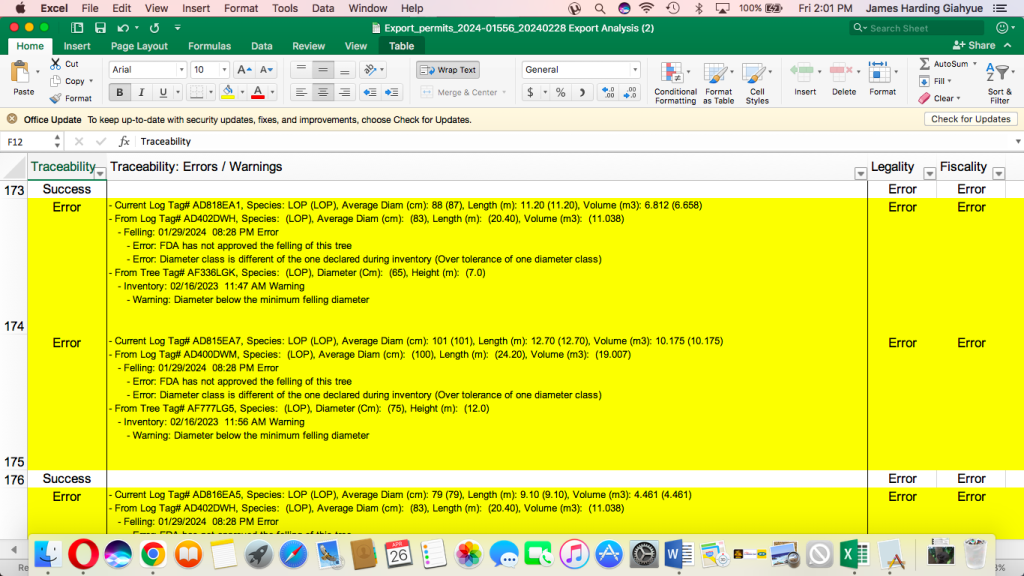
The investigation was based on an analysis of the consignment generated by the FDA log-tracking computer system or LiberTrace. The report cited a screenshot of LiberTrace’s history of West Water Group (Liberia) Inc.’s logs.
Details of the red-flagged logs appeared on the export permit and a National Port Authority document. That proved the FDA did not ensure West Water corrected the issues LiberTrace raised before sanctioning the export.
West Water had harvested the logs in the District Three B&C Community Forest in Grand Bassa County, where the Chinese-owned company has a 15-year logging contract with villagers. The logs were loaded on the MV Tropical Star, a cargo ship that left Liberia on March 16 and arrived in China on May 26, according to the vessel information provider Marine Traffic. Satellite images show cranes offloading the logs.
The second part of this series found that West Water owed the community forests in Bassa and another in Nimba over US$100,000, a violation of a payment regulation.
The FDA dismissed the investigation, calling it an “intentional misinterpretation” of the facts, and an alleged smear campaign.
But additional evidence gathered from three visits to the forest and interviews with villagers knowledgeable about West Water’s operations corroborates the first investigation. Also, a relook at the LiberTrace analysis and other documents provided additional clues.
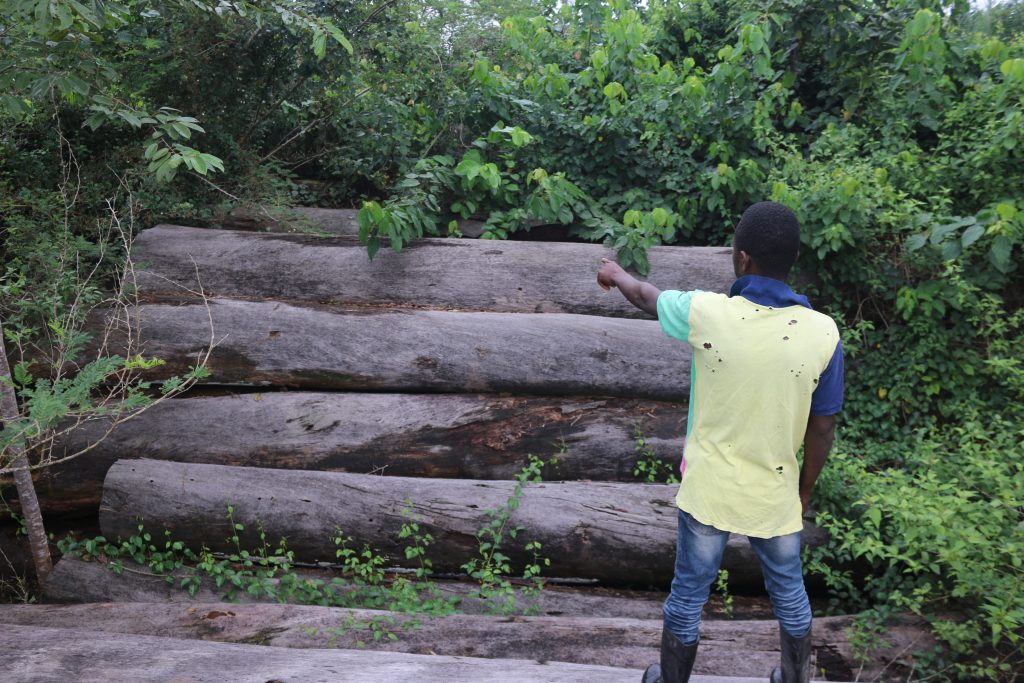
The DayLight traced several of the problematic logs to the stumps of trees from which they were harvested, using identification tags from the LiberTrace document. Once reporters matched the tag of red-flagged logs in the document to stumps, they measured the corresponding stumps with a tape rule, videotaping the process.
For instance, reporters traced one tree tagged “AF402RXT” that was red-flagged for multiple problems, including its size. When the reporters measured it, the reporters found the diameter of the tree was 65 centimeters. That is 10 centimeters less than the figure on the export permit and 15 centimeters less than the FDA-approved size for that species, dahoma (Piptadeniastrum africanum).
‘We will be the loser’
Unlike the tree stumps, reporters faced no difficulty in finding other pieces of evidence of undersized logs. A sea of immature logs with West Water tags decorated the forest and the roads leading to it.
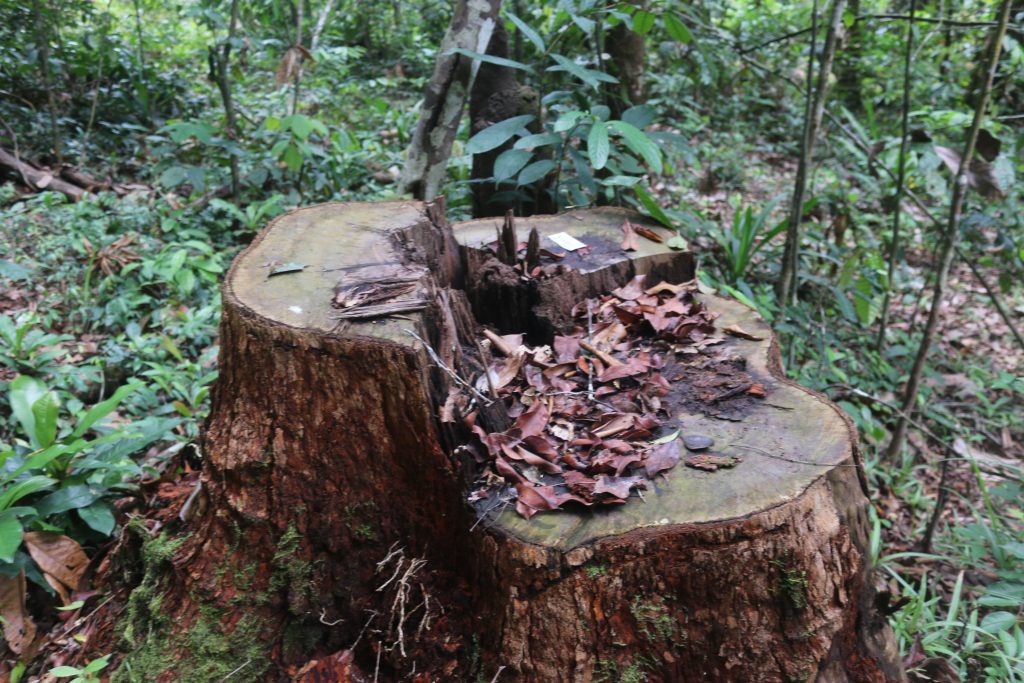

Villagers, including those knowledgeable about West Water’s operation, said undersized logs were a normal thing there.
“I saw many trees that did not reach the complete diameter and they harvested them,” said Isaac Doe, a villager and an ex-West Water worker.
“If they keep cutting the under-diameter trees, we will set up [a] roadblock and stop them,” said Isaac Jimmy, an elder of that region.
“We will be the loser when they continue felling young trees,” added James Kawee, one of the community forest leaders.
Evidence of undersized logs lay bare in the forest but hid in plain sight in the LiberTrace analysis. When reporters took a closer look at the document, they made a stunning discovery.
Of the 413 problematic logs, 217 were below their harvesting sizes, known in forestry as the diameter cut limit. A total of 266 had been harvested without the FDA’s approval, the sources of 46 logs were unknown, and 55 had no GPS coordinates for tracking purposes. Each log had multiple legality issues.
All of the problematic logs were harvested in two weeks between late January and mid-February, during the post-elections transition.
There were five rounds of harvesting. The first occurred on January 29 with a mammoth 251 logs. It was followed the next day with 11 and the day after 25. Harvesting resumed on February 12 with 106 logs and the following day with 10.
Some villagers said they witnessed West Water felled and transported the wood at night. Their accounts are consistent with LiberTrace, which shows some felling occurred between 8 pm and 9 pm.
“I want the government to implement their rules and regulations to stop them,” said John Flomo, an elder in Paygar Town, one of 14 towns and villages that own the forest.
Reporters filmed West Water trucks transporting logs at night on a major route during their third visit to the forest. FDA’s regulation on timber traceability prohibits nightly transport of logs on public roads. West Water did not respond to queries for comments on this story.

LiberTrace is a crucial component of timber traceability or the chain of custody system. Meant to prevent illegal wood from entering domestic and international markets, the system traces logs from their origins to their final destinations. The European Union and the United Kingdom funded LiberTrace.
But that was not all the evidence The DayLight gathered. The investigation found that West Water did not have a harvesting certificate when the felling took place. The one Merab shared with The DayLight was not signed by then Managing Director Mike Doryen or a deputy.
The invalid certificate ran from March to September last year and the valid one runs for the same period this year. Once more, this proves that all 413 logs West Water harvested in January and February this year were illegal, even by the FDA’s lowered standards.

That likely explains why LiberTrace red-flagged the dates all the 413 problematic logs were felled. It also appears to explain why the FDA’s legality verification department (LVD) provided a flawed breakdown of LiberTrace’s warnings.
“Out of 797 logs, 50 percent are traceable with red label because of diameter…,” Gertrude Nyaley, the Deputy Managing Director for Operations, who was the technical manager of LVD at the time of the export, handwrote the document.
“Based on the above results, we recommend that West Water… export permit be issued.”
Nyaley reduced the magnitude of the issues LiberTrace highlighted. The computer had listed up to 13 legality issues with the logs, including unauthorized harvesting.
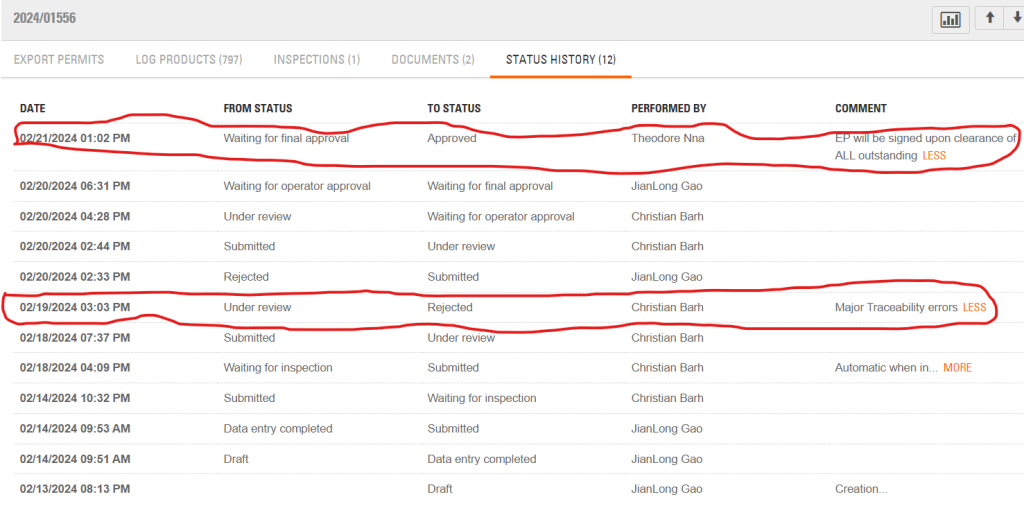
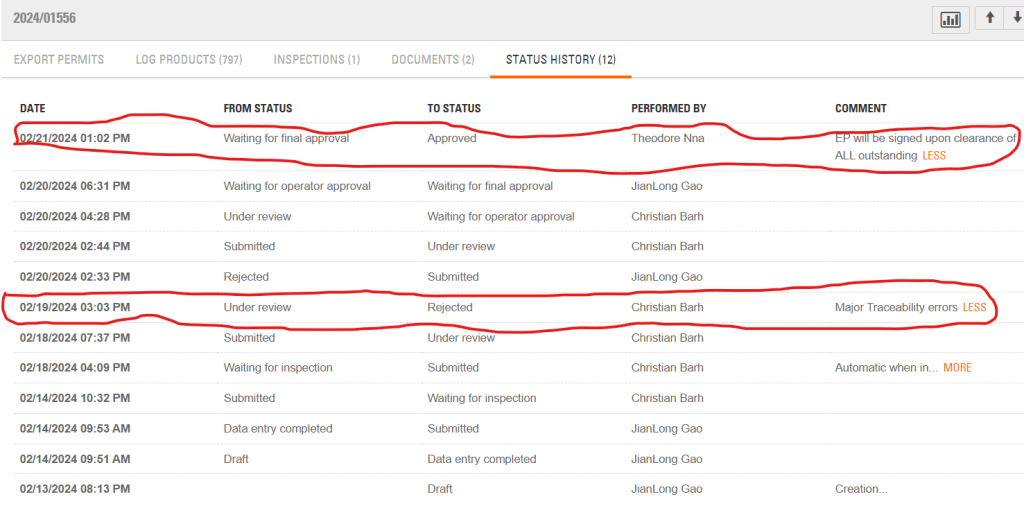
The LiberTrace screenshot of the logs’ history shows West Water requested the export several hours before conducting the last harvesting.
Christian Barh, an LVD staff, rejected the request on February 19, 2024, by 3:03 PM, citing “major traceability errors.”

The next day, Barh accepted the request and passed it on to Theodore Nna, SGS’ forestry project manager. SGS is a Swiss verification firm that built and powers LiberTrace. Nna okayed the request less than 48 hours later. Rudolph Merab would approve the illegal export in one of his first acts as the Managing Director of the FDA.
Nna flouted SGS’ sustainability standards by endorsing the export. The standards ensure traders and users that the timber they trade or use comes from sustainably managed forests, according to SGS’ website. Nna did not respond to emailed queries for comment on this story.
Cover-up exposed
Merab claims the errors and warnings were usual, and that some of them were corrected. “After log yard verification and physical scaling, the log will be exported,” Merab told The DayLight in a letter. “It’s a normal occurrence and we are open to [verifying] such an occurrence with you the DayLight.”
Those comments are not backed by facts. The export permit spec, which details the information on each log in the consignment, shows the issues were never fixed.
“[Merab’s] explanation is in line with the SOP but in contradiction of the action on the export permit approved,” one chain of custody expert, who prefers anonymity over fear of retribution, said.
“If and only if measures were taken to do the timber yard correction, this action could not reflect in the approved export permit.”
The expert was referencing LVD’s standard operating procedures (SOPs), which require errors corrected at different levels, not only during export. For instance, the FDA’s felling SOP requires LVD to ensure a company corrects any errors LiberTrace catches upon felling.


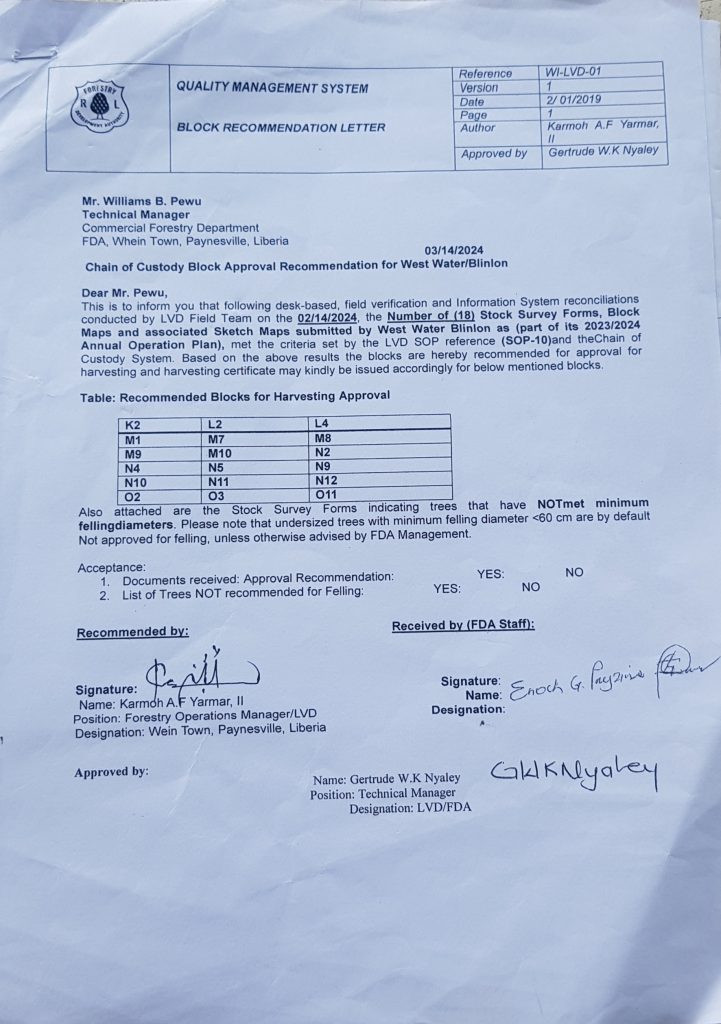
Several documents the FDA provided contain inconsistencies, suggesting they were forged as part of an all-around cover-up.
One document is dated 2019 and 2024, listing Nyaley as head of LVD. Nyaley was the technical manager of the community forestry department that year, appointed to LVD in 2022. And West Water did not have a contract in Grand Bassa or anywhere in 2019, at least not a direct one.
Another document puts West Water’s export (3,275 logs) above its production (2,782). That is a difference of 493 logs.
Unlike for the initial investigation, Merab did not respond to The DayLight’s queries for comments on this story. He did not grant the newspaper’s access to West Water’s contract and harvesting maps, guaranteed under various legal provisions. The FDA had said it would not return future questions from DayLight regarding export permits.
By approving the export, the FDA violated its laws.
Cutting trees without authorization and harvesting undersized logs constitute a fine per the FDA’s confiscated logs regulation. A violating company faces a fine of two times the value of the illegal logs and a public auctioning of the wood. That means West Water would have paid more revenue for the March export.
Jonathan Yiah, the lead forestry campaigner at the Sustainable Development Institute, criticized the FDA for not confiscating the logs and undermining LiberTrace’s credibility.
“Focusing on enforcement,” Yiah said, “will demonstrate and ensure both revenue generation and sustainable management and harvesting of our forest resources.”
[Emmanuel Sherman and Philip Quwebin contributed to this report]
The story was a production of the Community of Forest and Environmental Journalists of Liberia (CoFEJ).