Top: A graphic depicting an illegal logging operation conducted by a group of six Sierra Leonean loggers for a Liberian company called Libfor Forest Corporation. The DayLight/Rebazar Forte
By Mark B. Newa
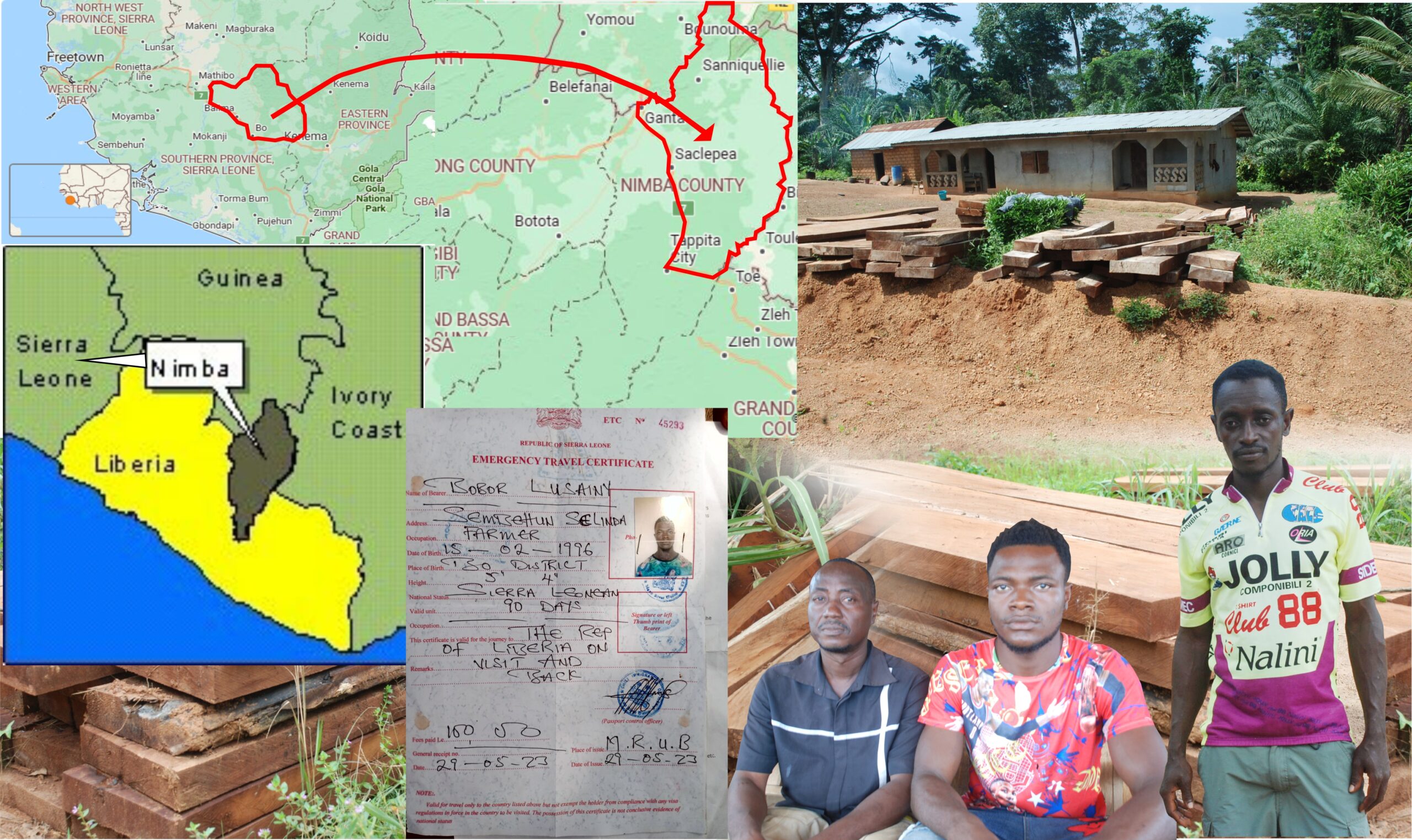
KARNPLAY – A group of Sierra Leoneans, hired by a Liberian businessman, are conducting an illegal logging operation in a forest in Nimba County, according to documents, interviews and photographs.
With the help of locals, the operations are producing thick timber near the Ivory Coast border in Karnplay, Gbelay-Geh District.
The Sierra Leoneans’ operations violate the Chainsaw Milling Regulation, which bars non-Liberians from working in the subsector, evidence shows. Their products go against the standard measurement for planks, matching a form of logging recently banned by the Forestry Development Authority (FDA).
From Bo to Nimba
In early May, a representative of Libfor Forest Corporation, met Aruna Kamara, Bobson Lusainy, Philip Sungu, Sorie Bangura and two other men in the Sierra Leonean eastern province of Bo. The representative asked them to travel to Liberia and serve as chainsaw operators of Libfor, a small-scale logging company established in 2021.
By May 30, the six men headed to the Liberian border at Bo Waterside. There, the company’s representative arranged for emergency travel certificates for the men, according to the documents seen by The DayLight.
Not long after, the men found themselves in Ganta, some 303 miles away from home. They signed a contract. Tejan Jalloh, a Sierra Leonean who works for Libfor, signed for the company, while Sungu signed for the men.
They agreed to harvest timber, with a payment of L$600 per piece, according to their contract, obtained by The DayLight.
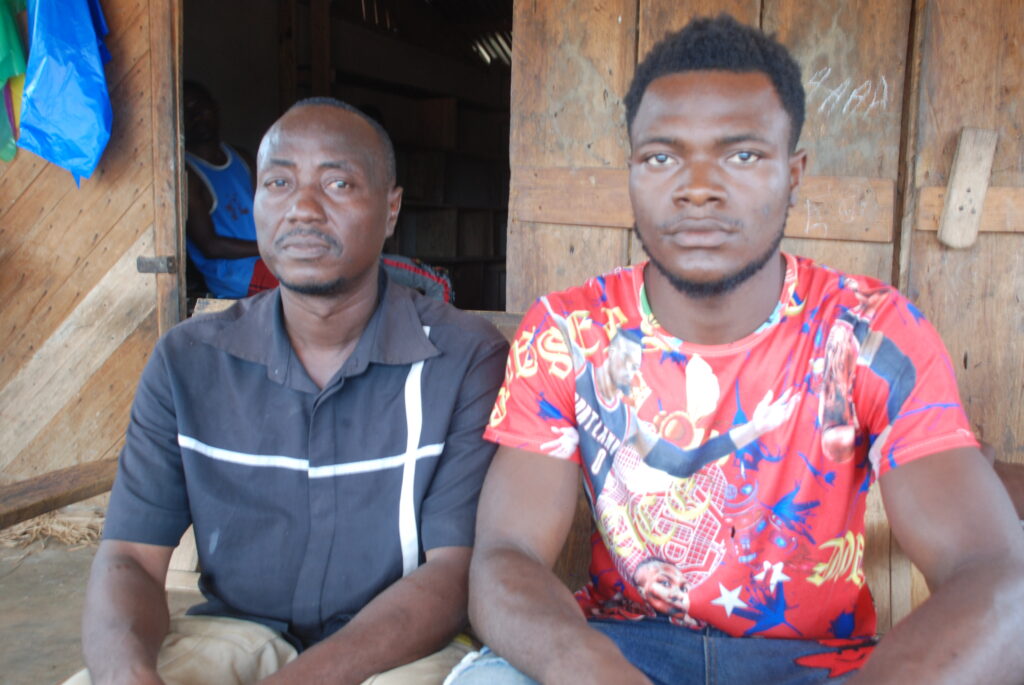

The six men were then transported to Trorplay, a village in the Gbeh-Somah Clan, Gborplay Chiefdom.
They cut down trees on the farms of individual farmers between L$1,500 and L$3,000. They have already harvested 460 planks, according to Kamara, the oldest of the men.
“We hauled some on the road and the rest are in the bush,” Kamara, the oldest of the six men, told The DayLight in an interview.
‘Kpokolo’
Our reporter photographed stacks of the illegal timber by roadsides and in several other locations. They match the profile of Iroko, a durable wood species used for shipbuilding, furniture and outdoor construction. Currently, it is selling up to US$390 on the international market.
Community leaders are unhappy with the loggers for three reasons. First, they think the Sierra Leoneans are buying the trees too cheaply. Second, they feared that cutting the trees would make their community vulnerable to rainstorms. Locals use the Iroko trees for herbs.
“The tree can protect our towns and villages from strong wind. Iroko is a very strong wood and it also has a kind of value for traditional herbs,” said Anthony Wopleh, a farmer in Trorplay.
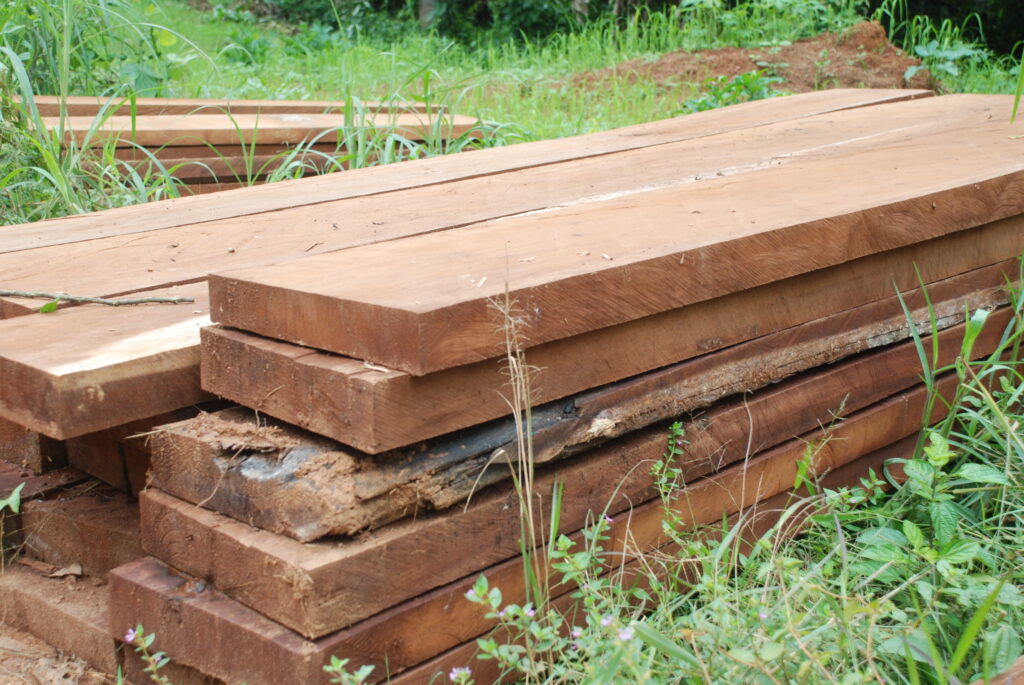


“This is a tree that our people use to heal sicknesses like rheumatism and it is very helpful in treating other diseases,” Wopleh added.
“Cutting down the trees and carrying them like that, [with] nothing remaining here for our community is not good. Look at our roads, from here to Karnplay is so bad,” said Samson Zreakpa, a chief in the Gbeh-Somah Clan.
Local chainsaw millers are also upset with the Sierra Leoneans for “undermining” their efforts. “The guys have infringed on our movement and they have entered into the bush, telling our people negative things,” said Emmanuel Gongor, who ran illegal operations in the region exposed earlier this year by The DayLight.
Amara Fofana, the sole owner of Libfor, based on its article of incorporation, denies the allegations. “My power saws are registered with the local chainsaw union, and they know me good,” Fofana told The DayLight via phone.
‘I cannot fight the government’
The accusations against the Sierra Leoneans may be true or not but the illegality of their operations is obvious. Under the Chainsaw Milling Regulation, non-Liberians are debarred from making planks. The subsector, started by ex-combatants following the end of Liberia’s bloody civil wars in 2003, is primarily meant to supply the domestic market and provide jobs for Liberians.
Also, Libfor does not have a chainsaw milling permit and the farmers who are selling to Sierra Leoneans do not have the authorization to do so. However, that level of violation is commonplace in the subindustry. Apart from imposing fees on chainsaw millers, the FDA has failed to regulate the lucrative trade in its 20 years of existence.
Moreover, the size of the wood the Sierra Leoneans are producing is prohibited. Normally, the FDA allows only up to two-inch-thick planks in the subindustry, and not three-inch.

Over the last decade or so, the FDA secretly sanctioned the production of oversized timber, commonly called “Kpokolo.” In February, the agency announced it had “banned” kpokolo, following a series of reports by The DayLight. The agency admitted it had permitted kpokolo producers to supply sawmills across the country but that permit was abused.
In the phone interview, Fofana said he was harvesting Iroko to make furniture at his own sawmill. He said he expected some machines soon.
“I want to make furniture in Caldwell to compete with the Lebanese businessmen in Monrovia,” Fofana, said via phone, revealing he had 20 chainsaws in the Nimba belt.
Fafona added that he had hired Sierra Leoneans because he could not find any Liberian to do the work. Later, he claimed that Liberians were lazy, dishonest and counterproductive to his company’s vision.
“There are no good operators in Liberia,” Fofana claimed. “This is why somebody brought me those guys to work for me.”
Over the debarment of non-Liberians, Fofana argued that the ECOWAS protocol empowered the Sierra Leoneans to work anywhere in Liberia.
That claim is wrong. People from ECOWAS countries are entitled to a 90-day stay in Liberia. However, they are not allowed to work without a residence permit, according to the Aliens and Naturalization Law. If they work without residence permits—as in the case of the Sierra Leoneans—they violate the law. In fact, the Sierra Leoneans should have obtained work permits before felling their first tree, according to the Decent Work Act.


Apparently conceding, Fofana said he would send the men to Gormahplay in the Bu-Yao District, toward the Ivory Coast border at Butuo.
Further in the interview, Fofana lied that he was not aware his Sierra Leonean workers were harvesting oversized planks. However, The contract his company signed with the Sierra Leoneans exposed him. It clearly obligates the men to harvest timber measuring three inches in thickness, 13 inches in width and 15 feet in length.
Told of the clause of the contract that speaks about the height of the wood, Fofana conceded.
“Actually, I do not know that one,” he told our reporter. “When the wood is above the size required by law, I will reduce it because I cannot fight the government.”
It was easier for Fofana to have said those words than it is done in forestry. Illegal timber harvest is punishable by a fine of three times the industry’s price of the wood and the total cubic meter of the wood in question. Violators could also face a six-month prison term or both fine and imprisonment, according to the Regulation on Confiscated Logs, Timber and Timber Products.
This story was a production of the Community of Forest and Environmental Journalists (CoFEJ).




Facebook Comments