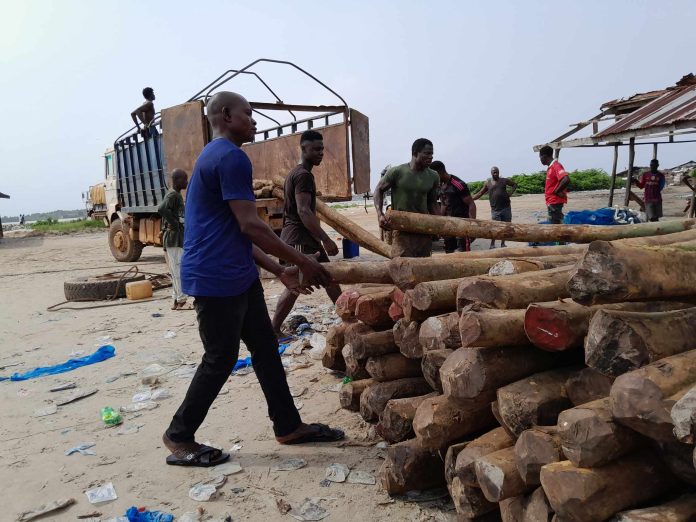
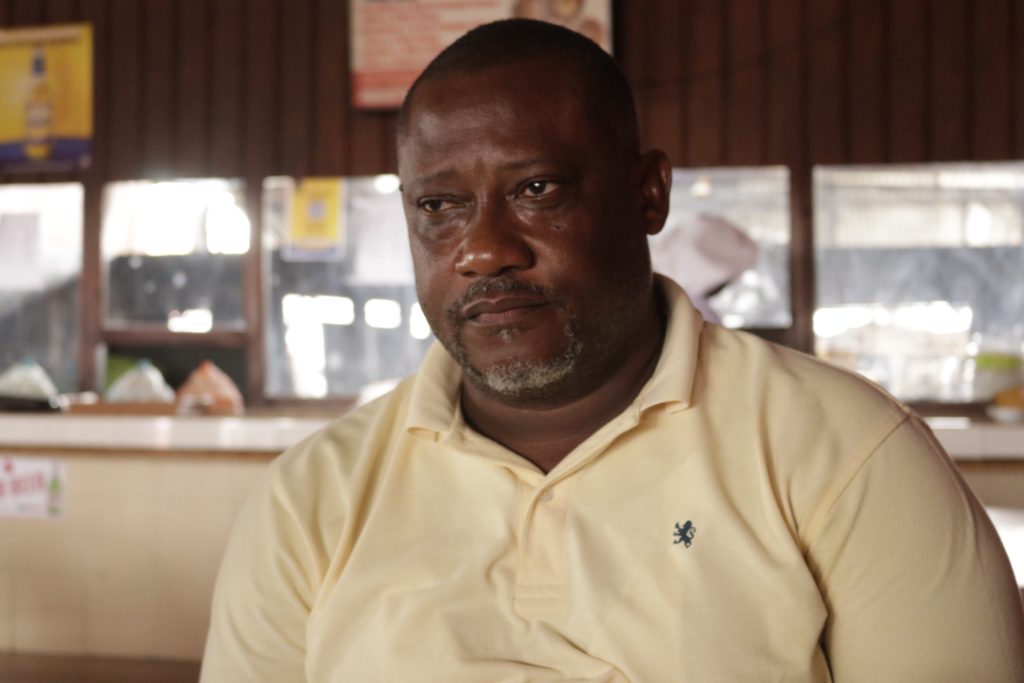
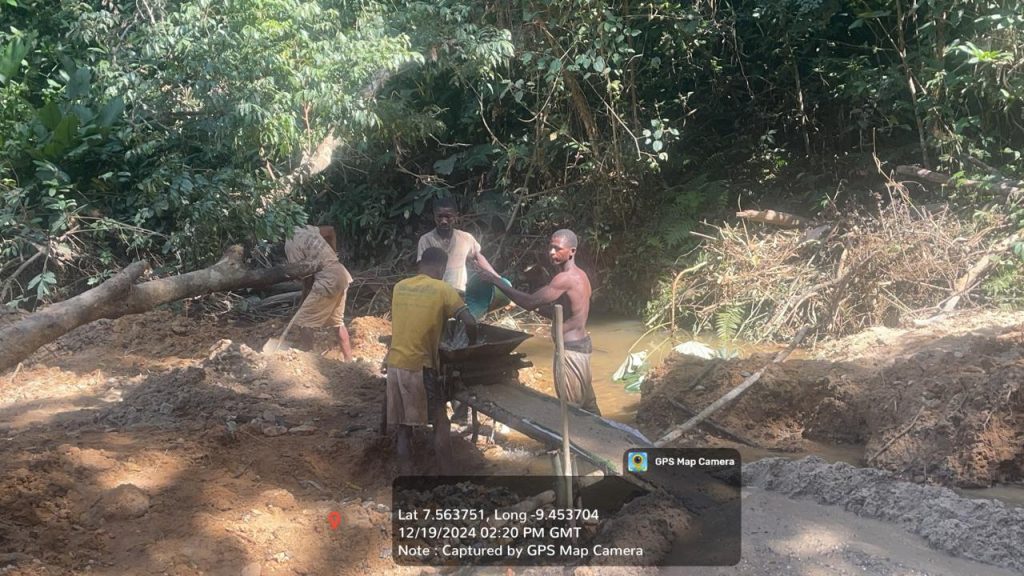
Top: Men offload chewing sticks at a beachfront in Greenville, Sinoe County in January 2024. File Picture: Anonymous
By Emmanuel Sherman
BARLOME TOWN – A truck with chewing sticks parked near an open field. Some of the sticks lay on the ground. It had been parked for three weeks in Barlome Town on the Grand Bassa-River Cess highway. The sticks had been transported from Nimba County and uploaded there.
“I am waiting for my boss,” said Obed Amoah, an attendant to the 37-ton truck with Ghanaian license plate GR-5774.
Reporters had happened upon a major player in the shadowy world of chewing stick trafficking. In 2021, the Forestry Development Authority (FDA) imposed a moratorium on chewing sticks to curtail the clearcutting of the species. However, The DayLight found evidence, that the FDA has been issuing chewing stick permits amid the moratorium.
The evidence shows that chewing stick pushers pay the FDA at different levels, with poor, rural communities receiving a small portion. The sticks are transported in smaller trucks and are loaded into large trucks similar to the one The DayLight saw in Barlome Town.
Amoah’s boss, Isaac Pyne, pays several fees: an annual registration, a permit license, an export permit, and a waybill—fees for transporting forest products.
Pyne had to travel to Drodonewein, a town in Nimba County to get the sticks. He would mobilize 30 to 40 men to harvest the sticks.
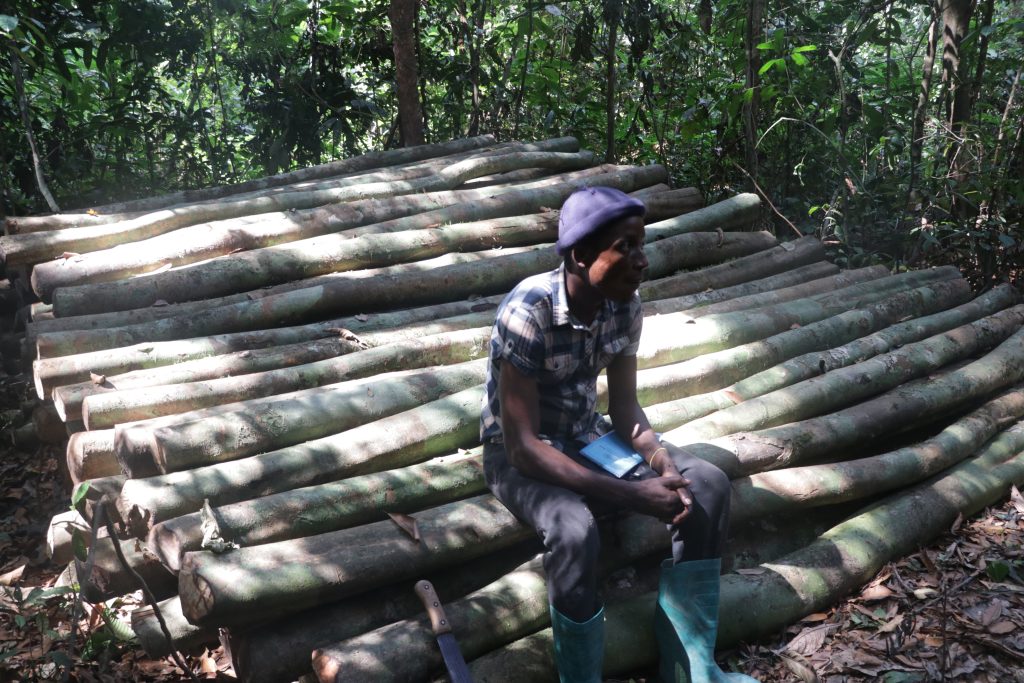

Pyne’s company, Winner Peace and Love Chewing Sticks reached an agreement with Dordonewien for LD40 per stick. The townspeople signed the deal, hoping it would develop the community, as it lacks a hand pump, toilet and clinic.
In all, Pyne harvested 1,000 chewing sticks and made one shipment. However, he has yet to meet all his obligations, having paid the community L$11,360.
“We were thinking we would have gotten the L$40,000 so that we could renovate our peace hall,” said Emmanuel Gibson, the youth chairman of Dordonewein. Pyne acknowledged his debt to the villagers and insisted he would pay the balance.
On commission
Once uploaded into the large truck, Pyne transports the sticks to the border via Pleebo or Laguatuo, and then to Ghana, Togo, or Senegal through the Ivory Coast.
Zebedi Bonwin, another chewing stick businessman in Buchanan, corroborated the route. Reporters had caught up with Bonwin’s truck in a town on the outskirts of Buchanan.
Bonwin revealed he also transported chewing sticks via the sea. “I used the boat one or two times,” he said. Other people The DayLight interviewed in Bassa, River Cess and Sinoe confirmed Bonwin’s sea route account. The newspaper obtained photographs of men offloading chewing sticks on a beachfront in Greenville, Sinoe County.
The DayLight also gathered evidence that chewing sticks and bitter kola are sourced from Bassa, River Cess, Bong, and Lofa, and transported to Guinea. Our reporter visited several locations in the counties, conducting interviews, and photographing warehouses and border crossings.
In Ghana, Pyne sells his sticks to mostly market women in the Ashanti Region of Kumasi, who pay him a commission. The women retail the sticks in shreds, charging US$2.50 or US$3.00 for a pile.
Prominent in African and Asian communities, chewing sticks (Salvadora persica) are used for tooth cleaning and as a herb. With their use dating back to prehistoric times, chewing sticks can be as effective as toothbrushes in removing dental plaque and caries.

Moratorium
Pyne, Bonwin, and other businesspeople are violating the 2021 moratorium on chewing sticks—with the aid of the FDA.
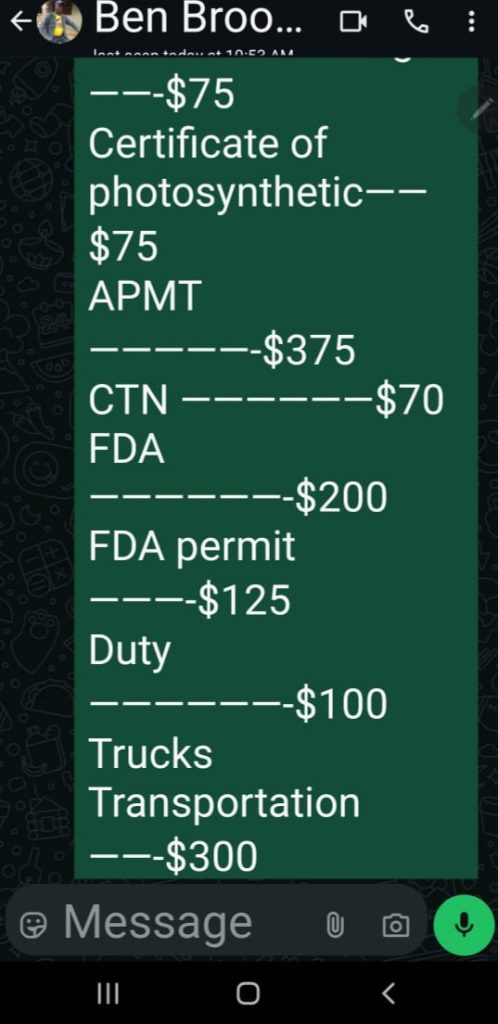
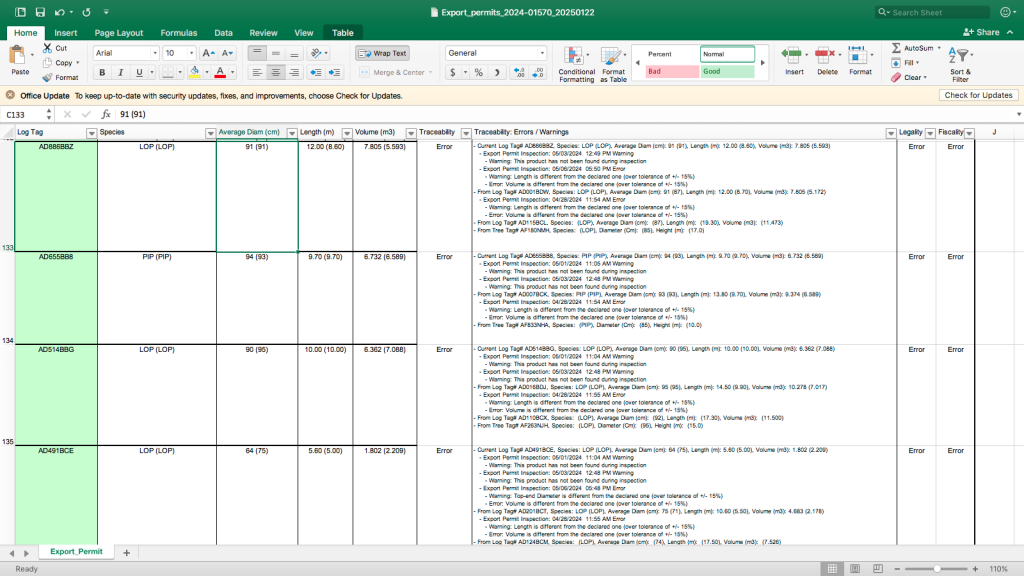
Pyne provided three receipts that show different kinds of payments to the regulator. One for US$250 dated February 20, 2024, for annual registration. Another one recorded two payments for 630 pieces of chewing sticks with an accumulated volume of 15.908 cubic meters and an export permit fee of US$1,073.70. Two receipts document US$50 for an export license and a waybill of L$12,600. The waybill had been issued at the FDA’s Big Joe Town checkpoint in Grand Bassa on January 17, 2025.
Similarly, two official receipts The DayLight obtained reveal transactions in January last year. The two receipts show L$6,000 and L$9,000 payments to the FDA from one Emma Emmanuel in Greenville Sinoe County.
The evidence establishes Pyne paid some of the fees to an FDA account at the United Bank of Africa (UBA). This payment procedure violates the National Forestry Reform Law and the Regulation on Establishing a Chain of Custody System.
The regulations require that all forest fees be paid to the government’s account at the Central Bank of Liberia. The measure was installed to safeguard public funds, following decades of mismanagement, which, interestingly, continues today.

That mode of payment is similar to the one that fueled block wood or kpokolo, heavy and compact timber blocks illegally harvested, containerized and exported via land or sea. Following a decade of facilitating the trade, the FDA finally banned kpokolo in 2022. Last year, the regulator also banned the issuance of a certificate that facilitated the trade, according to minutes of an FDA board of directors meeting in July last year.
Pyne and Bonwin claim the government has lifted the moratorium.
“The FDA said the moratorium is lifted and we are starting again,” said Bonwin, who runs the Garraway Enterprise Inc. in the Buchanan suburb of Lower Harlandsville.
But that claim contradicts the facts. The FDA board meeting’s minutes prove the moratorium remains in place. In the meeting, the board agreed to lift the moratorium only upon a review of the Regulation on Non-Timber Forest Products (NFTPs) for the public to participate, an underlining principle of forestry reform.
“All other certificates signed by the [Managing Director] become null and void,” according to the document. “FDA needs to invite all those involved for a way forward.”
Though the board discussed local and national benefits of lifting the moratorium, there is no evidence the regulation has been reviewed, or a consultation has taken place. The FDA’s website does not have such information. Key civil society actors, including the Botanical Products Association of Liberia, which makes awareness of the protection and trade of NTFPs, said they did not participate in any such event.
Formulated in 2008, the NTFPs regulation covers chewing sticks, charcoal, rattans, bitter kola and other forest products other than timber. It was meant to provide income opportunities for local communities and the government, create awareness of NTFPs, and classify them for research purposes.
But it was not sufficiently community-centric, necessitating a review for a possible amendment or replacement.
“Once the [law] gives the community the right to own, manage, and protect the forest, and non-timber forest products are in the forests,” said Bonathan Walaka of the National Union of Community Forest Management Body.
“So, there should be a kind of benefit-sharing scheme for a community to receive benefits from that.”
Philip Parker, the chairman of the FDA’s Board of Directors, did not reply to questions, and neither did the FDA management. This is the second time Parker, whose duty is to hold the FDA to account, has ignored The DayLight’s inquiries. Similarly, the FDA’s refusal to respond adds to its silence on such matters, and an unwillingness to provide public information.
[Harry Browne contributed to this Investigation]