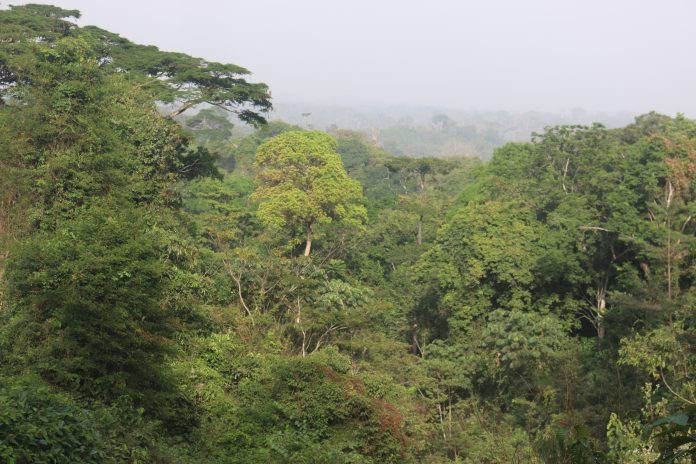
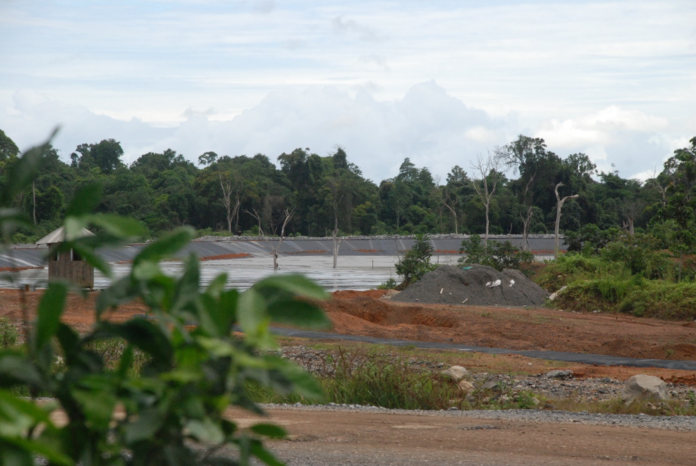
Top: Korninga B Authorized Forest Community has sued Bea Mountain Mining Corporation for US$4.3 million in damages for alleged illegal entry and destruction of its woodland. The DayLight/James Harding Giahyue
By Esau J. Farr
TUBMANBURG, Bomi County – A community forest in Gbarpolu County has rejected Bea Mountain Mining Corporation’s proposal for a settlement in a US$6.3 million lawsuit against the company.
Bea Mountain proposes to pay the Korninga B Community Forest US$100,000, a US$65,000 mobile sawmill and a pair of chainsaws, according to the proposed settlement document seen by The DayLight.
Korninga B and Bea Mountain had agreed to the settlement in 2022 but the company pulled out of the arrangement, prompting the community to go to court. Locals filed for US$6.3 million action of damages over Bea Mountain’s alleged unauthorized entry and destruction of the forest.
Under the settlement agreement, seen by The DayLight, Bea Mountain offers to pay Korninga in two installments. The company agrees to deploy five staff to train the same number of townspeople to operate the sawmill, according to the document.
The settlement proposal also prohibits Bea Mountain from working in the forest and gives Korninga possession of the trees that Bea Mountain cleared.
Aaron Mulbah, the chief officer of Korninga, said they rejected the proposal because they had incurred expenses as a result of their lawsuit. “They have to go above that,” Mulbah told The DayLight.
Cllr. Kunkunyon Wleh Teh, Bea Mountain’s lead lawyer, declined an interview with The DayLight.
Verdict and Retrial
Korninga B’s lawsuit accuses Bea Mountain of felling over 2,800 logs to make a passage through the 78,624-acre forest in the Bokomu District to its mining sites, according to court documents. Bea Mountain is also accused of harvesting logs from the area to construct bridges, throwing some in valleys while burying others.
The company denies any wrongdoing, saying it only mined in areas covering its licenses, and that the community should instead pay it damages for allegedly obstructing its operations.
Following more than five months of legal battle, a six-man jury found Bea Mountain liable for wrongdoing.
But the court granted Bea Mountain’s petition for a retrial on grounds that jurors failed to take witnesses’ testimonies into account and ignored inconsistencies in testimonies, calling the US$5 million damages “grossly disproportionate.”
In early March 2022, Bea Mountain Mining Corporation allegedly illegally entered the Korninga B Community Forest in Bokomu District and felled several trees.
Under the Community Rights Law…, locals own and comanage forests adjacent to their communities alongside the Forestry Development Authority (FDA). The law is a breakaway from the past, where only the government and companies had a say in forestry. It guarantees locals’ right to forestland and prohibits unauthorized entry and use of forest resources.

Before going to court, Korninga informed Bea Mountain of its ownership of the forest and Bea Mounting’s alleged illegal actions. The two parties agreed that the company would pay the community US$165,000 for the damages and other things.
Ruth Varney, a representative of the Forestry Development Authority (FDA) in the western region, had compiled a report on the alleged damages with the company’s funds, court documents show.
But Bea Mountain pulled out of the arrangement, which also included Keyah Saah, the Superintendent of Gbarpolu County. Angered by that, Korninga filed a US$4.3 million lawsuit against the company at the 16th Judicial Circuit Court in Bopolu, Gbarpolu County.
Bea Mountain’s defense team asked the court to dismiss the case. Its lawyers argued that locals did not have the right to sue the company and that it had legal mining licenses to operate in that area.
The three medium-scale mines in question are located in the same region as the Korninga B Community Forest. The licenses of two of the mines are held by MNG Gold, a company owned by Mehmet Nazif Günal, the Turkish billionaire who also owns Bea Mountain. The license for the other is held by Gbarpolu Mining Corporation, a Liberian-owned firm.
Prosecution lawyers led by Atty. Alston Armah asked the court not to grant the defense lawyers’ petition. Prosecution lawyers argued that Korninga had the authority to file the lawsuit. They added that the mining licenses were not owned by Bea Mountain.
The court in Bopolu agreed with Korninga and denied Bea Mountain’s petition, and the case proceeded. However, it was transferred to the 11th Judicial Circuit Court in Tubmanburg, Bomi County after another petition by defense lawyers.

There, prosecution lawyers told the court Bea Mountain broke the Community Rights Law… “The destruction of the forest with no knowledge of the legal community forest is causing [the community] pain, suffering, mental anguish and distress,” one court filing read.
Lawyers of Bea Mountain counterargued that the company and a partner legally obtained the three mining licenses it operates in that region. They said the Korninga forest leadership did not have the authority to sue the company, only its ancestral land leadership had. They said the investigation conducted by Varney was not legal or binding because she was not authorized to do so.
The court heard testimony from Yanquoi Dolo, the head of the FDA’s legal department. “The FDA did not communicate any official assessment report involving Korninga B Community Forest,” Dolo told the jurors.
Following final arguments, the six-man jury handed down a unanimous verdict against Bea Mountain in October last year. The jurors held Bea Mountain liable for US$1,311,401.21 in special damages and US$3 million in general damages.
Three days after the ruling, the company filed a petition for a new trial, citing inconsistencies in witnesses’ testimonies and that the jurors ignored some of their evidence.
Prosecution lawyers argued that documentary evidence and testimonials were sufficient to have the company liable for the damages. They said the jurors’ guilty verdict matched the evidence produced during the trial.
But, this time, the court ruled in favor of Bea Mounting, ordering a retrial. Judge Ciapha Carey said the inconsistencies favored the company as well as the fact not all the trees in question were scaled.
Unsatisfied with the ruling, lawyers representing Korninga B petitioned the Supreme Court for a review of the case. The high court affirmed Carey’s ruling for a new trial.
Mulbah said Korninga was awaiting a retrial.
“We are asking international partners, NGOs to help the community people in our case with Bea Mountain,” Mulbah said. “Bea Mountain feel that they have money… but the law is there.
The law will provide for us.”